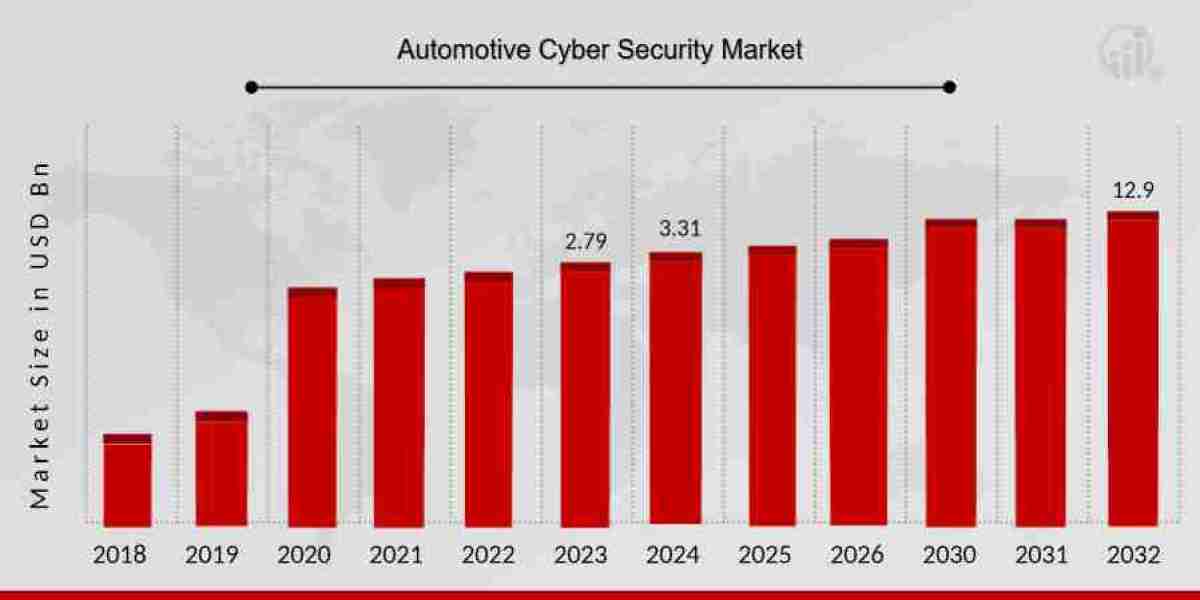
Introduction
In recent years, the automotive industry has undergone a remarkable transformation, with the integration of advanced technologies such as connected vehicles, autonomous driving systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities. While these innovations promise enhanced safety, convenience, and efficiency, they also expose vehicles to a new wave of cybersecurity threats. As the automotive landscape evolves, the urgency to address these vulnerabilities has never been greater.
The Rise of Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles are equipped with various sensors, software, and communication systems that allow them to interact with other vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud. This connectivity enhances features such as navigation, real-time traffic updates, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). However, it also opens the door for cybercriminals to exploit these systems.
Hackers can potentially gain unauthorized access to a vehicle's network, compromising critical functions such as braking, steering, and even engine control. The infamous Jeep hack in 2015, where hackers remotely took control of a vehicle, highlighted the vulnerabilities present in modern automobiles and served as a wake-up call for the industry.
Emerging Threats
As vehicles become more interconnected, the types of cyber threats continue to evolve. Some of the most concerning threats include:
Remote Hacking: Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in vehicle software to gain remote access. This could lead to unauthorized control of critical vehicle functions or data theft.
Malware Attacks: Just like computers, vehicles can be infected with malware. This malicious software can disrupt vehicle operations or steal sensitive information.
Data Breaches: Connected vehicles collect vast amounts of data about their users, including location, driving habits, and personal preferences. A breach in this data can lead to privacy violations and identity theft.
Denial of Service (DoS): Attackers can overwhelm vehicle systems with excessive requests, rendering them inoperable. This could lead to dangerous situations on the road.
Industry Response
In response to these growing threats, the automotive industry is taking significant steps to bolster cybersecurity. Manufacturers are investing in advanced security measures, including:
Regular Software Updates: Just as smartphones and computers receive regular updates, vehicles must also be updated to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security features.
Robust Encryption: Implementing strong encryption protocols ensures that data transmitted between vehicles and external systems remains secure.
Security Testing: Manufacturers are conducting rigorous testing of their systems to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before vehicles are released to the market.
Collaboration: Automakers are working together, sharing information about threats and best practices to create a more secure automotive ecosystem.
Regulatory Measures
Governments and regulatory bodies are also stepping up to address automotive cybersecurity. In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has issued guidelines for manufacturers to follow, emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity in vehicle design and production. Additionally, the European Union is implementing regulations that require automakers to ensure their vehicles meet specific cybersecurity standards.
The Role of Consumers
Consumers also play a crucial role in automotive cybersecurity. By staying informed about their vehicles' features and potential vulnerabilities, drivers can take proactive steps to protect themselves. This includes:
Keeping Software Updated: Ensuring that the vehicle's software is regularly updated to the latest version.
Using Strong Passwords: For vehicles with connected services, using strong, unique passwords can help prevent unauthorized access.
Being Aware of Phishing Scams: Consumers should be cautious of suspicious messages or emails that may attempt to trick them into providing personal information.
Future Outlook
As the automotive industry continues to innovate, the importance of cybersecurity will only increase. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technology will introduce new challenges and opportunities in the realm of cybersecurity. Manufacturers must remain vigilant and adaptive, continually evolving their security measures to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
In conclusion, while the integration of technology in vehicles offers numerous benefits, it also presents significant cybersecurity challenges. The automotive industry, regulatory bodies, and consumers must work together to ensure the safety and security of connected vehicles. By prioritizing cybersecurity, we can enjoy the advantages of modern automotive technology while minimizing the risks associated with it. As we move forward, the commitment to cybersecurity will be essential in shaping the future of transportation.